Cleaning Eggs With Sound
Clean your fruits, vegetables…and eggs…without chemicals


For years, small flock owners have asked for an alternative way to clean their eggs—if they clean their eggs at all. Every state has its own regulations with regard to the sale of eggs. Regardless of the state, eggs must be clean if they are to be bartered with or sold.
I cannot count how many times small flock owners have inquired about better ways to clean eggs. The simplest method is to wash the egg under running water with a soapy sponge to remove tough spots on a dirty egg. For removing stains, you can use fine grit sandpaper. But some folks do not do much other than placing eggs under water.
A clean egg is one with no adhering foreign material or prominent stains.
There is a relatively undiscovered product, though, that is accessible to small flock owners to help with cleaning eggs. This device has been used for cleaning fruits and vegetables, but this has not really been explored for cleaning the eggs of small flock owners.
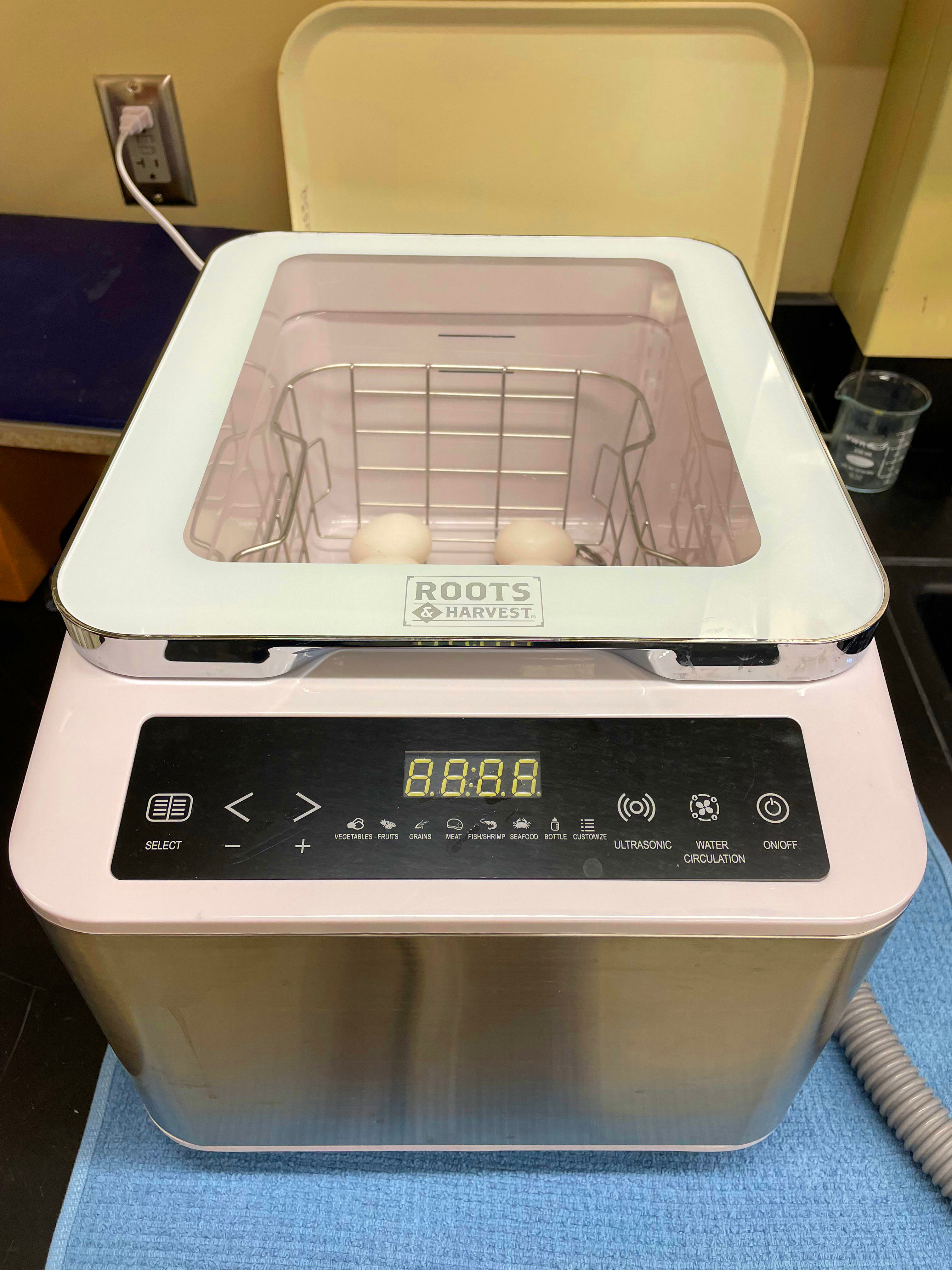
Roots & Harvest makes a countertop “sonicator” (an abandoned trademark for an ultrasonic cleaner) which I found intriguing. After looking through the manual, I spotted that it said eggs could be cleaned in the sonicator.
Being a microbiologist, I was intrigued and started designing an experiment to see if the sonicator was effective in decreasing the microbial load on the outside of eggs.
It holds several dozen eggs, the exact number of which will vary depending on the egg size that your flock is currently laying.
How it works
A sonicator uses high frequency sound waves to create cavitation bubbles in water. Eggs are placed in a basket and put into the sonicator chamber. The chamber is filled with water and the lid is closed.
The sonicator is turned on and set to the 8-minute “fruits” setting and allowed to run.
There is a impeller that moves the water around and the eggs during cleaning. When the cycle is done, you open the lid and lift out the entire basket. The eggs dry quickly in the basket or you can set them out on a towel to dry faster. Then the eggs are ready for packaging and refrigeration.
How to test effectiveness
I wanted to test the effect of the sonicator in its ability to decrease the bacteria load on the outside of eggs.
I also wanted to see if the sonicator had any effect on the interior quality of the eggs.
Sound waves from a sonicator means that the sound waves can pass through the protective outer layer of the shell. I wanted to know if the sound waves affected the quality of the egg white or if it affected the strength of the shell.
What did we test?
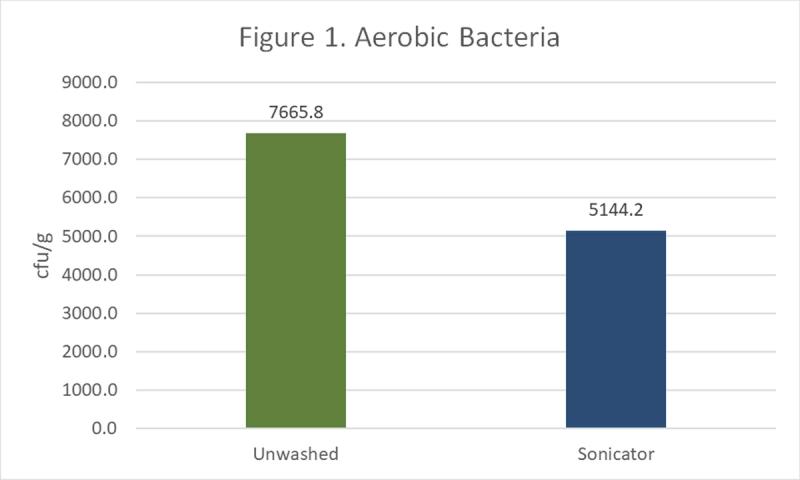
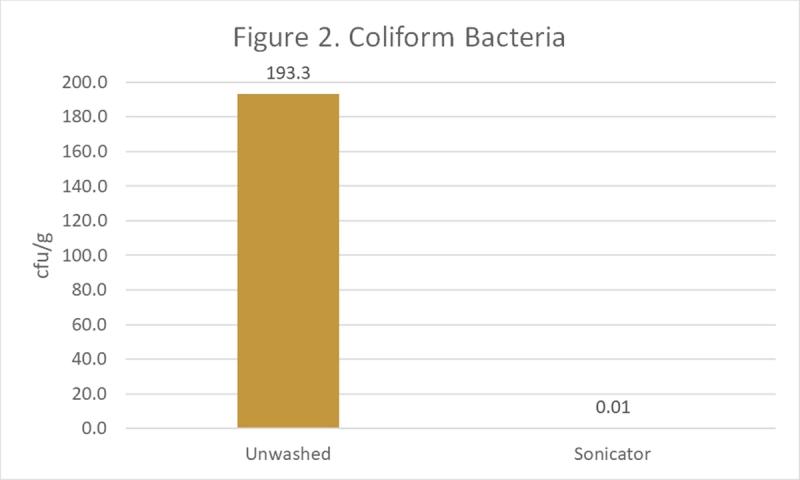
We tested the outside of the eggshells for two groups of bacteria. The first group is aerobic bacteria, which includes bacteria that grow in the presence of oxygen. The second group is coliforms which includes E. coli.
For the aerobic bacteria (Figure 1), the sonicator reduced the bacteria numbers by 33% compared with eggs that were unwashed. The sonicator also was able to provide a nearly 100% reduction in the amount of coliforms (Figure 2).
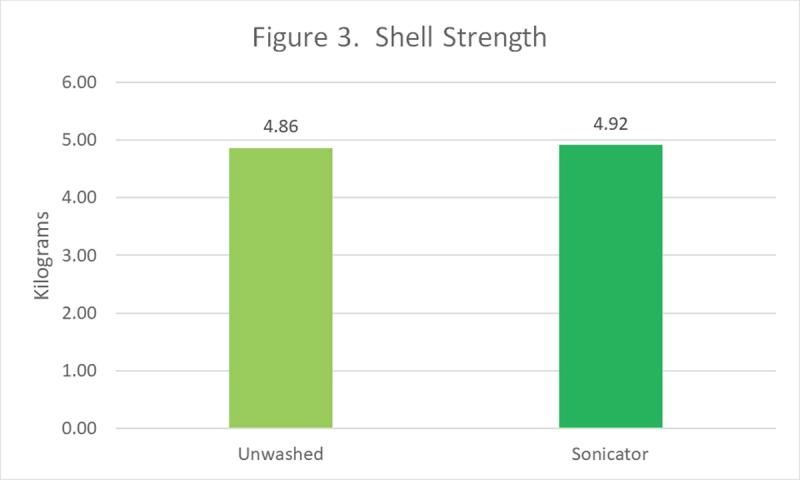
The shell is the main source of protection for the contents of the egg. Since the sonicator’s effectiveness is through the use of cavitation, and the shell comes into contact with the cavitation bubbles, the shell strength was tested. Figure 3 shows that eggs in both groups yielded similar results, regardless of the group in which they were placed.
Bottom line: Shell strength was not adversely affected by the sonicator.
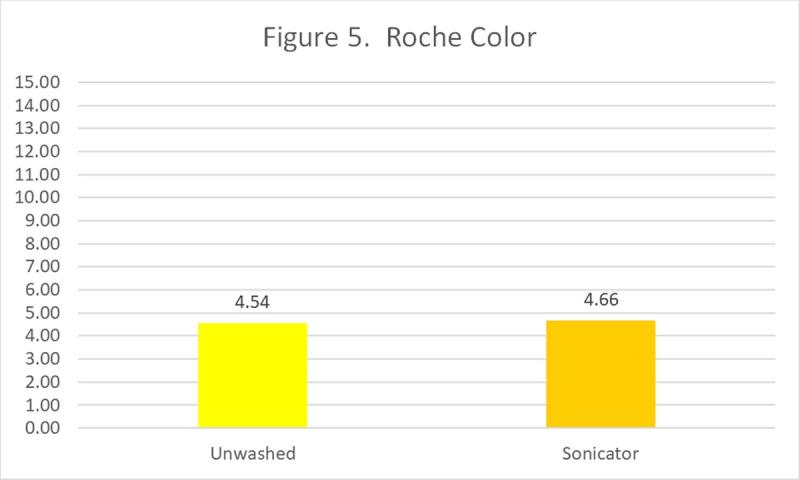
The Haugh Unit is a measure of albumen, or egg white, quality. High quality albumen stands tall and close to the yolk. Low quality albumen is weak, watery, and does not perform well in holding the yolk stable in the center of the egg.
Additionally, low quality albumen fails to perform well in several measures of cooking performance.
Figure 5 indicates that Haugh Units were not adversely affected by the sonicator.
Why you should use it
The Multi-Purpose Ultrasonic Cleaner by Roots & Harvest was easy to use for eggs. The sonicator did not have any adverse effects on either shell or interior quality of eggs.
The sonicator reduced the number of spoilage and fecal-associated bacteria on the outside of the shell. Overall, the effect of the sonicator on eggs was beneficial.
About the author
Dr. Brigid McCrea, PhD, is a poultry scientist who has worked with small flock owners for more than a decade. Her expertise is being utilized at Auburn University in the development of curriculum for 4-H Youth Development's Animal Programs.
Tags:Plain Talk

Chicken Whisperer is part of the Catalyst Communications Network publication family.











